A USB port is a standard interface found in a wide range of devices, including smartphones, tablets, and computers, and plays a crucial role in the world of electronic gadgets. This essential component enables seamless connection, data transfer, and power supply between devices. It features male and female connectors with coupling portions, allowing for wireless data transfer and power supply. USB ports are available in various shapes and sizes, such as USB-A, USB-B, USB-C, and USB Micro-B, each representing different generations of USB technology. Newer variants offer improved data transfer speeds and other enhancements. In the realm of smartphones, USB ports are necessary not only for charging and syncing data with a computer but also for connecting to external accessories like headphones, speakers, or storage devices. The latest USB standard, USB Type-C, provides users with faster charging speeds, quicker data transfers, and a more convenient, reversible connector design, ensuring the continued relevance and importance of USB ports despite rapid technological advancements.
Technical Specification of USB Port
| Features | Detail |
| USB Versions | USB 1.x, USB 1.1, USB 2.0, USB 3.0, USB 3.1, USB 3.2, USB 4 |
| Data Transfer Rate | USB 1.0 (1.5 Mbps)
USB 1.1 (12 Mbps) USB 2.0 (480 Mbps) USB 3.0 (5 Gbps) USB 3.1 (10 Gbps) USB 3.2 (20 Gbps) USB 4 (40 Gbps) |
| Power Delivery | – USB 1.x/2.0: Up to 500 mA |
| – USB 3.x: Up to 900 mA | |
| – USB Power Delivery (USB PD): Up to 100W | |
| Connector Types | – Type-A, Type-B, Type-C, Micro-USB, Mini-USB |
| Pin Configuration | Type-A: 4 pins
Type-B: 4 pins Type-C: 24 pins Micro-USB: 5 pins Mini-USB: 5 pins |
| Backward Compatibility | Generally supported across versions |
| Alternate Modes | USB Type-C supports alternate modes like DisplayPort, Thunderbolt 3, etc. |
| Cable Length | USB 1.x: Up to 3 meters (10 feet)
USB 2.0: Up to 5 meters (16 feet) USB 3.x: Up to 3 meters (10 feet) USB 4: Up to 0.8 meters (2.6 feet) |
History and Evolution of USB Ports
The Universal Serial Bus (USB) has been a fundamental component of modern connectivity since its introduction in the mid-1990s, providing a groundbreaking method for connecting peripherals at a speed of 12 Mbps. Throughout its development, USB has undergone various improvements to enhance its speed and functionality. USB 1.1 addressed early communication issues, while USB 2.0, introduced in 2000, set a new standard with a transfer rate of 480 Mbps, leading to the popularity of USB flash drives. The introduction of USB 3.0 increased speeds to 5 Gbps and introduced the USB-C connector, known for its reversible design. Subsequent versions, USB 3.1 and 3.2, further improved transfer rates up to 20 Gbps and refined power delivery features, despite some confusion caused by naming changes. The most recent version, USB4, released in 2019, offers speeds up to 40 Gbps and exclusively utilizes the USB-C connector, simplifying and enhancing the compatibility of the various devices that shape our digital world. This evolution highlights the technology industry’s continuous pursuit of more efficient and universally compatible connectivity solutions.
Types of USB Ports
USB ports have revolutionized data connectivity, with each type designed for different speeds, power outputs, and device compatibility. Here is an overview of the common types of USB ports you may come across:

1. USB Type-A
USB Type-A ports have long been a staple in the technology industry, serving as the standard USB connector since its introduction in the late 1990s. Known for their flat, rectangular shape, these ports have been essential for a wide range of devices, including computers, laptops, gaming consoles, smart TVs, and charging devices. Their design allows for a one-way fit, preventing incorrect insertion and ensuring a secure connection. Type-A ports are valued for their simplicity and durability, as well as their compatibility with various peripherals such as keyboards, mice, external hard drives, and flash drives. Despite the emergence of newer USB standards, the Type-A port remains relevant for supporting older devices and a wide range of accessories that rely on its reliable interface. With advancements in USB technology, Type-A ports have also seen improvements in data transfer speeds and power delivery, solidifying their importance in our digital lives for both technology enthusiasts and general users.
2. USB Type-B
USB Type-B is a well-known connector with a distinctive, almost square shape, commonly used to connect printers, scanners, and external hard drives to computers. It is valued for its reliability and sturdy design that prevents accidental misconnections, ensuring a stable and dedicated link for data transfer and device management. While it may not have the sleekness of the newer USB Type-C, USB Type-B has adapted to the changing technology landscape with USB 3.0 Type-B variants offering improved data transfer speeds important for efficient office workflows. Despite its decreasing popularity compared to USB Type-C, USB Type-B’s compatibility with a wide range of older devices solidifies its position as a key component in the USB ecosystem. Both tech enthusiasts and general users recognize the port’s essential role in maintaining swift and efficient performance from their devices, showcasing the enduring value of practical and purposeful design in the constantly evolving tech industry.
3. USB Type-C
USB Type-C is revolutionizing the technology industry with its advanced capabilities in data transfer and charging. This versatile connector is recognized for its reversible design, which eliminates the frustration of incorrectly plugging in cables. However, USB Type-C offers more than just user-friendly design; it provides high-speed data transfer rates of up to 10Gbps with USB 3.1 Gen 2 and supports USB Power Delivery (PD) for charging devices with up to 100 watts of power. This is a significant advancement for technology enthusiasts who require efficient charging and quick data synchronization. The port’s compatibility with alternate modes, such as DisplayPort or Thunderbolt 3, enhances its functionality, enabling video output and more. With the increasing adoption of this technology in smartphones, laptops, and other devices, USB Type-C is establishing a new standard for universal connectivity, where one cable can handle data, power, and video, ushering in a new era of connectivity for our digital lives.
4. USB Mini
In the rapidly evolving field of technology connectivity, the USB Mini port was introduced as a groundbreaking interface that was highly praised for its small size and versatility. This connector represented a significant advancement in the early 2000s, primarily used for mobile devices and cameras, and signaled a notable shift towards the miniaturization of hardware connections. Despite being surpassed by the more advanced USB Micro and USB-C ports, the enduring presence of the USB Mini in older equipment highlights its robust design and its role in transitioning from the larger USB Type-A and B connectors to more compact and user-friendly formats. Providing a combination of power and data transfer capabilities for its time, the USB Mini port continues to symbolize the constant innovation in the technology industry, laying the foundation for the sleek and multifunctional connectors that are popular among tech enthusiasts today.
5. USB Micro
For users of electronic devices, the Micro-USB port represents a significant milestone in the development of mobile connectivity. Introduced in 2007, this port featured a 5-pin design and a unique asymmetrical shape that prevented incorrect insertion, making it a durable and reliable option for charging and data transfers in a variety of portable electronics. Serving as the standard connector for numerous smartphones, tablets, and digital cameras, particularly in the early 2010s, the Micro-USB, specifically the Micro-B variant, supported the USB 2.0 protocol and enabled transfer speeds of up to 480 Mbps. Despite being surpassed by the reversible and faster USB-C, many devices still include the Micro-USB port, highlighting its previous widespread use. Its continued relevance in the technology collections of enthusiasts emphasizes the role it played in improving device compatibility and the broader USB technology ecosystem.
USB Port Versions and transfer Speeds
Understanding the different versions of USB ports is essential for mobile app developers who need to guarantee optimal data transfer speeds for their applications. Below is a detailed explanation of each version and its corresponding capabilities.

1. USB 1.0 (1.5 Mbps)
For individuals who have an interest in gadgets and phones, the history of USB is quite fascinating. It all began with USB 1.0 in January 1996. This initial iteration of USB revolutionized the way devices were able to connect, boasting transfer speeds of up to 12 Mbps at its peak and 1.5 Mbps at its slowest. This marked a significant improvement over previous methods of device connectivity. Despite the existence of newer, faster USB versions, USB 1.0 played a crucial role in simplifying the process of connecting devices by eliminating the need for separate software for each device and establishing the familiar USB shape that is still in use today. It laid the foundation for the rapid USB connections that are now ubiquitous. For those interested in the history of technology, the introduction of USB 1.0 represents a pivotal moment in ensuring seamless device compatibility and user-friendly operation.
2. USB 1.1 (12 Mbps)
In the evolution of USB technology, USB 1.1 is recognized as a significant milestone that played a crucial role in early smartphone connectivity and gadget interfacing. Introduced in 1998, it had a transfer rate of 12 Mbps, known as Full Speed USB, which was a substantial improvement from its predecessor, USB 1.0. While newer technologies now offer faster speeds, USB 1.1 remains important in the history of technology as it marked the beginning of seamless digital connectivity that we enjoy today. For casual smartphone users, USB 1.1 represents simplicity and reliability, while tech enthusiasts appreciate its role in laying the groundwork for the USB revolution. Although it is no longer commonly used in modern devices, understanding USB 1.1 can provide valuable insights into the rapid advancements that have transformed the technological landscape in the smartphone and gadget industries.
3. USB 2.0 (480 Mbps)
USB 2.0, also known as Hi-Speed USB, provides a consistent data transfer rate of 480 Mbps, making it a versatile standard for a variety of peripherals such as cameras, speakers, and storage devices. It strikes a balance between functionality and speed, meeting the needs of smartphone users and tech enthusiasts. While newer USB versions offer faster rates, the widespread use of USB 2.0 ensures compatibility across numerous devices, making it essential for gadget collectors and everyday smartphone functions like charging and file management. Its impact on user experience and device design remains significant, making it a focal point for those involved in the smartphone and tech accessory industry.
4. USB 3.0 (5 Gbps)
USB 3.0 has revolutionized data transfer for smartphone users by providing a SuperSpeed interface capable of up to 5 Gbps. This represents a tenfold increase in speed compared to USB 2.0, showcasing a significant advancement in connectivity technology. This enhancement benefits not only tech enthusiasts and app developers requiring faster file transfers and improved app performance, but also everyday users appreciating quicker charging times. As smartphones become more powerful, the integration of USB 3.0 underscores the industry’s dedication to enhancing data management and user convenience. With its high bandwidth, handling large files is effortless, ensuring devices operate at their maximum potential. The widespread adoption of USB 3.0 in newer gadgets is establishing a new standard for data transfer speeds, making it a crucial feature for individuals seeking optimal performance from their mobile technology.
5. USB 3.1 (10 Gbps)
USB 3.1, also known as SuperSpeed USB 10 Gbps, is a transformative force in smartphone connectivity, offering a staggering transfer speed of 10 Gbps. This advancement brings a substantial performance boost, providing tech enthusiasts, mobile app developers, and casual users with a seamless and efficient experience. The introduction of the “SuperSpeed+” bus under this specification ensures quicker file transfers, rapid charging, and a smoother mobile workflow, catering to the insatiable demand for speed in our digital lives. As the ecosystem of peripherals grows, the USB 3.1 interface not only enhances current usability but also future-proofs devices, ensuring compatibility with emerging technologies. For anyone looking to optimize their digital interactions, USB 3.1’s high transfer rate significantly reduces the time spent syncing photos, videos, and large files, thereby setting a new standard in what we expect from our smartphones’ connectivity capabilities.
6. USB 3.2 (20 Gbps)
USB 3.2 is a significant advancement in connectivity, providing smartphone users and tech enthusiasts with a transfer speed of 20 Gbps. This improvement allows for more efficient data management and transfer. The integration of advanced host controllers in USB 3.2 enables seamless data exchange between devices and PCI Express buses, doubling the bandwidth compared to previous versions. This enhancement benefits gadget collectors, early adopters, and mobile app developers, who can now debug applications and transfer large files more efficiently. Users can now enjoy faster backups and media transfers, enhancing their experience with smartphones and gadgets. The introduction of USB 3.2 represents a milestone in the evolution of Universal Serial Bus technology, ensuring swift and effective data management for those who prioritize speed and performance.
7. USB4 (40 Gbps)
USB4 is revolutionizing smartphone and gadget connectivity with its impressive 40 Gbps transfer speed, a significant improvement over previous standards. This new USB port technology reduces syncing time for large files, supports fast charging, and enables quicker backups, providing rapid access to content. Additionally, USB4’s compatibility with Thunderbolt 3 devices enhances mobile connections and offers a future-proof solution. The increased bandwidth is beneficial for mobile app developers for efficient testing and deployment, while gadget collectors will appreciate the superior video bandwidth and universal compatibility. USB4 is not just a technological advancement, but a comprehensive upgrade that enhances the mobile experience, making it a key feature for those interested in the latest smartphone and gadget trends.
What are the uses of USB Ports?
Here’s a list of common uses for USB ports:
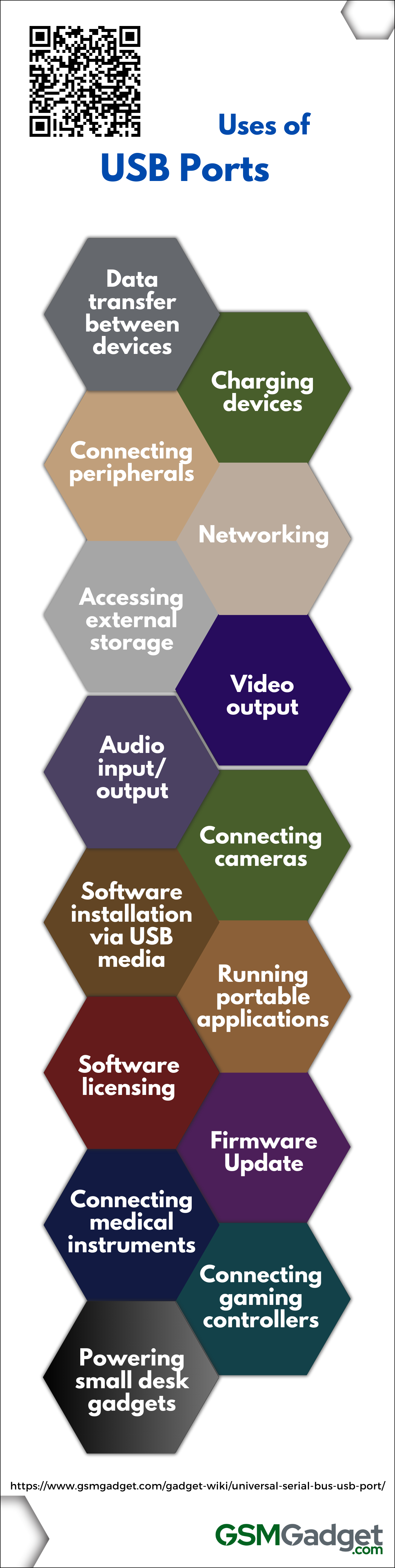
- Data transfer between devices: USB ports are essential for efficiently transferring data between smartphones, tablets, and computers. Their universal design allows for compatibility across various devices, making the synchronization process seamless for users.
- Charging devices: USB ports serve as a universal interface for powering a variety of devices, with smartphones and tablets being the most common. They offer a convenient and easily accessible way to recharge these gadgets, ensuring they remain operational throughout the day without the need for multiple chargers or ones specific to each device.
- Connecting peripherals: USB4 ports on smartphones enhance the device’s connectivity, providing speeds of up to 40 Gbps, which greatly improves tasks such as file transfers and peripheral integration. This advancement in USB technology turns your mobile phone into a versatile hub for productivity and entertainment, catering to the needs of both tech enthusiasts and professionals.
- Accessing external storage: USB ports on smartphones are essential for tech-savvy users, allowing for easy connection to flash drives and portable hard drives to expand memory and facilitate seamless file transfer, thus overcoming the limitations of internal storage capacity. This feature is crucial for individuals who frequently work with large amounts of data, including multimedia enthusiasts and mobile app developers.
- Networking: USB ports on smartphones are essential for tethering, allowing the device to function as a portable modem for sharing internet connections when Wi-Fi or Ethernet is not available. These ports also facilitate seamless file transfer and connectivity with other devices, enhancing the networking capabilities of mobile technology.
- Audio input/output: USB ports on smartphones are essential for improving audio experiences by enabling users to connect a variety of devices, ranging from high-end DACs to basic microphones. This enhances both sound input and output for individuals, including casual listeners and dedicated content creators. This versatile feature not only simplifies charging and data transfer but also enhances audio quality and recording options for audiophiles and podcasters.
- Video output: USB ports on modern smartphones have become a versatile tool, allowing both casual users and tech professionals to mirror their device’s screen onto larger displays, such as monitors and TVs. Through a simple USB-C to HDMI connection, these ports facilitate immersive media streaming and enable developers to efficiently present their mobile applications on a wider screen.
- Connecting cameras: USB ports on smartphones are an important feature for technology enthusiasts and photographers, allowing for the direct connection of cameras to quickly transfer high-resolution photos and videos, as well as provide live previews. This is beneficial for content creators who require fast sharing of high-quality images. This feature is attractive to both experienced mobile app developers and regular users seeking to enhance their digital media capabilities.
- Software installation from USB media: USB ports on smartphones have become a crucial feature for tech-savvy users, providing a fast and reliable method for installing software or performing system updates directly from USB media. This capability is particularly beneficial for individuals who prefer the tactile reassurance of physical media to manage their devices’ applications and operating systems, avoiding the need for wireless download.
- Running portable applications directly from USB drives: USB ports have become a fundamental component of technology for smartphone users, providing the convenience of running a wide range of portable applications directly from USB drives. This capability enables technology enthusiasts and mobile app developers to customize and optimize their digital experience, ensuring that their essential tools and preferred settings can easily transfer across multiple devices.
- Upgrading firmware for devices connected via USB: USB ports are an essential tool for smartphone enthusiasts, providing a direct connection for firmware upgrades that can improve device performance and enhance security. By connecting to a USB port, users can quickly install the latest software updates, ensuring their devices stay up-to-date with technological advancements.
- Using USB dongles for software licensing or security authentication: USB ports on smartphones enable improved security and software license management by utilizing USB dongles. These dongles provide a secure connection for two-factor authentication, ensuring that only authorized users can access sensitive mobile applications. Additionally, these devices support OTG functionality, allowing tech-savvy individuals and mobile app developers to easily protect personal data and intellectual property.
- Connecting gaming controllers and accessories: USB ports on smartphones serve as important connectors for gaming controllers and accessories. They not only offer fast charging options but also enhance mobile gaming by providing the tactile precision found in traditional consoles. This improves the gaming experience for both casual and dedicated players. The integration of external devices with mobile technology pushes boundaries, allowing gamers to fully immerse themselves in their digital adventures with improved control. Developers can also optimize their apps to meet higher gaming standards.
- Connecting scientific and medical instruments: USB ports play a crucial role in enhancing the functionality of smartphones for healthcare professionals and technology enthusiasts. They allow for the direct connection of scientific and medical instruments, enabling real-time data analysis and promoting innovative mobile diagnostics. This integration creates opportunities for convenient health monitoring and scientific research on-the-go, utilizing the computational power of mobile devices.
- Powering small desk gadgets: USB ports on smartphones function as a convenient power source for various desk gadgets, such as LED lamps and mini fans, improving the utility of the workspace and combining entertainment with practicality for technology enthusiasts. This capability turns your smartphone into a versatile charging station, ensuring that your personal devices stay operational and easily accessible.
